Visual Perception For Robotics And Autonomous Driving: Implicit Kalman
Visual Perception For Robotics And Autonomous Driving: Implicit Kalman

Visual perception is still a challenging issue. Most deterministic techniques rely to track feature based on iterative and statistical approach like the Method of Least Squares and Kalman Filter. These algorithms are quite unstable because it requires that within the sampling distance between the image time series there is no similar object nearby which produces a redundant situation where the distinct feature in the images could be mixed up with the redundant neighbor. This falsifies the final result of deterministic perception algorithms.
Meanwhile in the past few years there have also been depth estimation algorithms. They work somewhat not so bad, but as the name implies they are „estimates“ which often contains much fluctuation in the estimated depth or a very low resolution which makes them hard to implement into functional safety systems where a false positive may cause harm to human life.
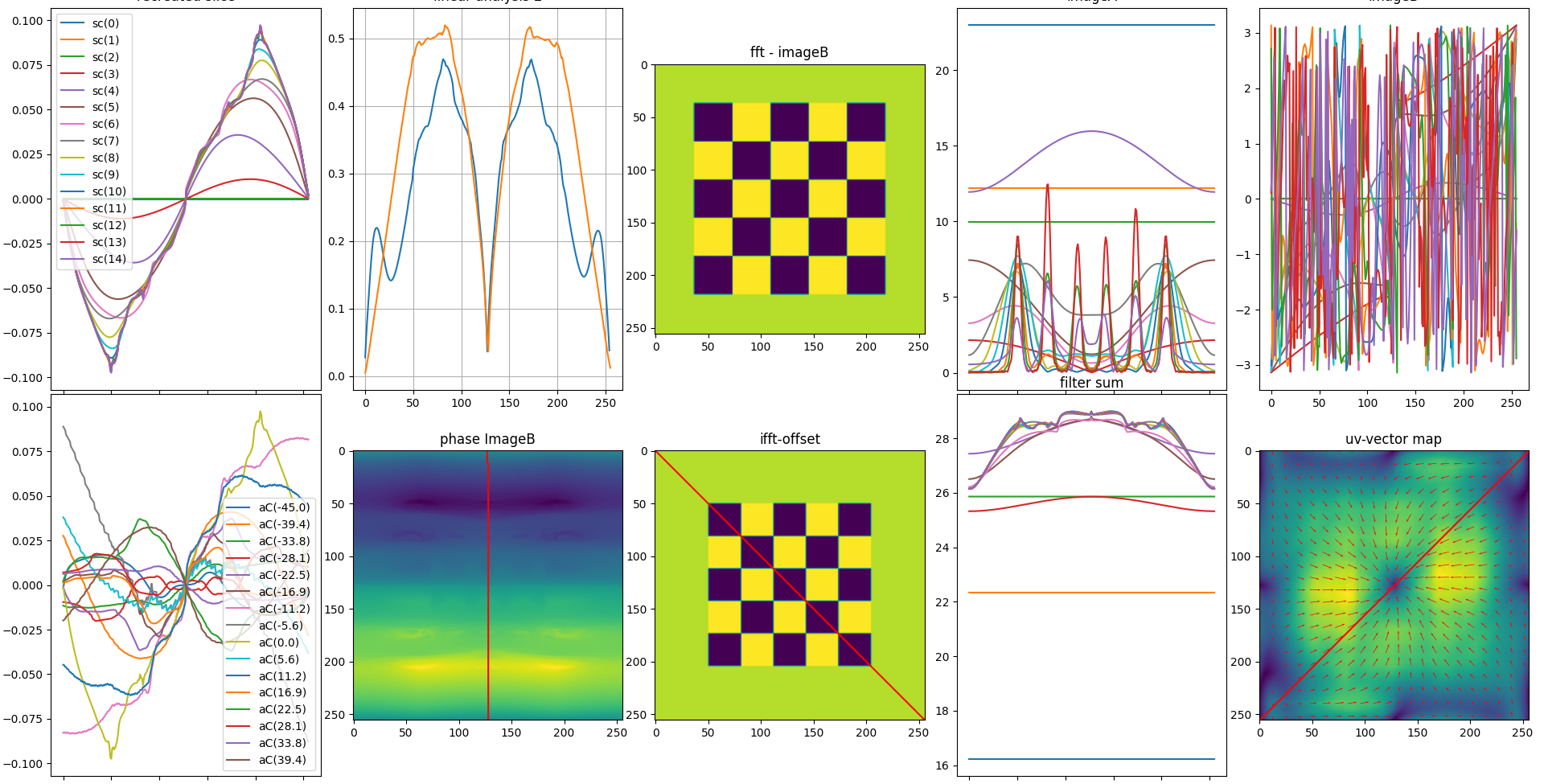
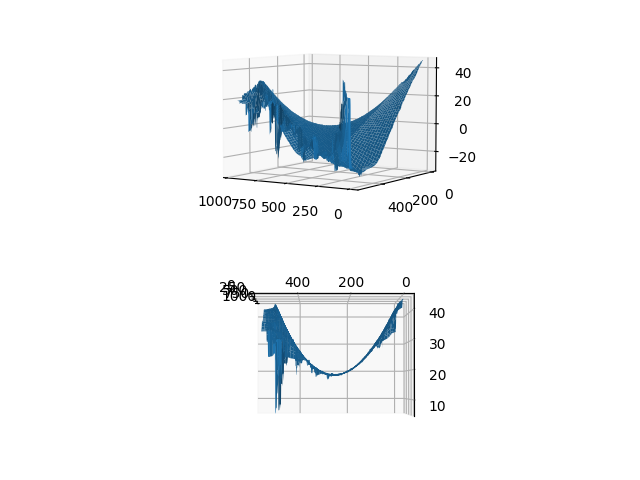
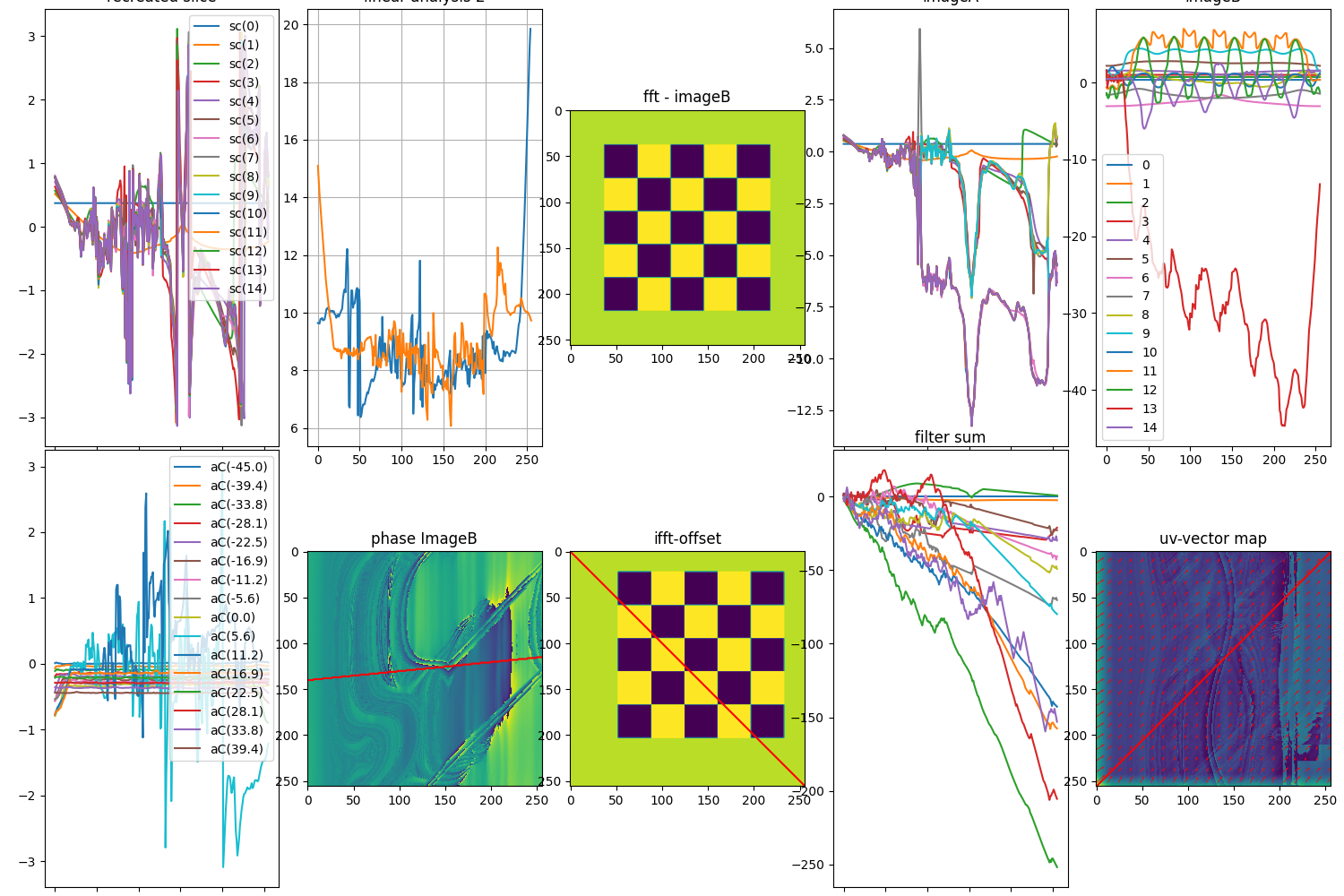
Therefor we invented Implicit Kalman. It’s a perception algorithm which looks for phase shift on different frequencies. It disassembles an image in a multi-frequency resolution pyramid via Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and detects the phase shift in the image for each part in the frequency spectrum of the image. This can not only produce a deterministic result of the Motion in a time series of images but due to its deterministic behavior the functional safety can be proven mathematically which makes it to a favorite for domains where human life is at risk
Follow @XIXUM Sponsor Watch StarProduct Features
Product Overview
Product Overview
Phase based motion detection by steerable filters supersedes feature based statistical search